A crucial aspect of search engine optimization lies in the technical infrastructure of the website, which relates to the crawlability of the website and the content required for the site to be indexed.
The state of technical SEO determines the condition of your website. For instance, if your site is invisible, insecure, or slow to load, search engines may skip it altogether when selecting a page to display in organic search results.
Technical SEO can reveal the reasons for poor rankings and provide suggestions to solve the problem. This involves optimizing website infrastructure at the initial construction stage of a site or making alterations and changes to existing sites.
So what are the elements of technical SEO?
Website Load Speed
Website speed affects search rankings. Google judges the website loading response speed from spider crawling, Google browser data, and whether to use CDN, load balancer, and other factors. So, what are the effects of website loading speed on SEO optimization? Google has explicitly stated time and time again that site speed is a direct SEO ranking factor.
User Experience
The ultimate goal of website optimization is for the best user experience, for users browsing the website is to solve their demand. If a website loads too slowly, the user will directly close the website, thereby increasing the bounce rate.
Search Engine Spider Experience
If the loading speed of the website is too slow or the website cannot be opened, it will affect the crawling of search engine spiders. After a long time, search engines will know that the quality of the site is too low, and will not crawl the content of the website again. And this is how the load speed can affect website ranking.
Have Our Team Speed Up Your Site!
Site Architecture
Website architecture is the way pages are organized and linked. An ideal structure can help users and search engine crawlers easily find the content they need. But what makes website architecture important for technical SEO?
Help Crawlers Find All Pages and Build Indexes for Them.
If your page needs to be clicked several times from the homepage (or there is no link to any webpage), it will be difficult for Google to find and index the page. However, if your site is well structured, your pages link to each other through internal links and you have sensible navigation in place; then the crawler can find what it needs by following internal links.
Site Architecture Can Convey Authority
If a highly authoritative web page is linked to other web pages through internal links, the authority (page ranking) will flow to other web pages. In this way, it can help improve the rankings of the other pages.
Help Visitors Find What They Want Quickly
A good website structure can improve visitors’ satisfaction with the page experience. This in turn makes them more likely to convert, but it also makes them less likely to return to the original Search Results page, which is yet another positive signal to Google.
Mobile-friendly
With the rapid development and popularization of the mobile Internet, mobile is the new normal. Now the proportion of searching and browsing through mobile devices has reached 75%. After 2015, mobile traffic surpassed desktop traffic for the first time.
Therefore, Google launched the Mobilegeddon algorithm to support mobile-friendly websites, which means that mobile-friendly sites will be ranked first when searching on the mobile terminal.
Sitemaps
A sitemap refers to a page that specifies basic information such as a site’s structure, columns, and content descriptions. A well-designed site map should allow bots to quickly understand the structure and content of the site.
Sitemap Constructs A Good Pathway for Spider Crawling
The working mechanism of search engines is to release spider crawlers to the Internet every day to crawl new web pages, and then rank these pages according to their algorithm. if these sites at the node position cannot be well visited by crawlers, it will undoubtedly increase the burden on search engines, and of course, it will be difficult to crawl all pages of the site completely. The sitemap solves this problem very well.
The crawler first visits the robots.txt We write the address of the site map in the robots.txt, which is equivalent to telling the crawler to crawl the map first. There will be many other pages on the sitemap.
The Sitemap Can Effectively Increase the Inclusion Ratio of The Entire Site
Extracting all the hidden pages through the sitemap, search engine crawlers follow the links on the site map to crawl them one by one, which will increase the collection of the entire site. For two websites with the same total number of pages, the site with a sitemap has a significantly higher inclusion ratio than the site without a site map.
Duplicate Content
How duplicate content affects SEO optimization is often misunderstood. Some people say it will lead to punishment by search engines. There are also many misunderstandings about what a search engine penalty is.
Duplicate Content on The Internet is The Norm
First of all, the world of the Internet is full of repetitive content. When a web page references the content of other websites, it will inevitably repeat some content on the other website.
What is A Search Engine Penalty?
Search engines will not penalize pages with duplicate content. The so-called penalty refers to the search engine extracting the page from the index database, making it impossible for search users to find the page in any search query.
Search engines find that pages or websites involve improper human manipulation of search rankings, and then downgrade the webpage’s original ranking position, which is also generally regarded as a search engine penalty.
Not being punished does not mean being liked. Search engines do not like repeated web content, the reason is: Search engines believe that Query Deserves Diversity (QDD), should give search users a diversity of SERP results.
For search engines, duplicate web content is the same answer to the query put forward by search users, but the URL is different, and the content is roughly the same.
Therefore, search engines will only extract the best URL from the same answer and put it on the search ranking results page, and other identical answers will be screened out. And this filtered result is often misunderstood as a search engine punishment.
404 Pages
A 404 page is simply a page that is not working. Either the URL never existed, or does not exist currently. Having a lot of 404 pages indicates to Google that no one is really taking care of the website and that users will often be left hanging with a link click leading to nowhere.
One option many webmasters use is automatically redirecting any 404 to the homepage. Google refers to this as a soft 404 and strips most of the benefits. Other options people take are setting a custom 404 page which has special navigation and often a search bar to try and mitigate the UX issues associated with someone clicking a link to nowhere. This is definitely better from a user perspective, but not much better from an SEO perspective.
When it comes to 404’s and broken pages on your site, if you want better rankings then you really need to have a 0 tolerance for 404. Hunt them down, redirect them, fix them, or change the links that are directed there. Just don’t leave them.
Not even sure if you have broken links on your site? Schedule an audit with our team today!
301 Redirects
So if 404 is a broken page, then a 301 can be seen as a redirection. Similar to putting a mailing forwarding address when you move home, this process takes a URL that no longer exists, but makes a safety net for users and bots by stating which page should be accessed instead.
For example, if you have a page called example.com/awesome-offer-which-will-make-your-day but then your boss points out that your offer is actually so good it is going to ‘revolutionize your month’ and tells you the URLs must be changed, then you can set a redirect from example.com/awesome-offer-which-will-make-your-day to example.com/awesome-offer-which-will-revolutionize-your-month
Now if someone visits the old URL, their browser will automatically open the new one instead. This is of vital importance when a URL has specific organic rankings, and you want to change the URL to something new. Without a redirect in place, Google will just think that your page no longer exists and start sending the traffic it was gaining elsewhere.
Canonical Tags
When our webpage can be accessed through multiple URLs, we can tell the search engine the preferred URL among these multiple URLs through the canonical tag, that is, the specified URL that the content of your webpage wants to be displayed in the search engine.
This is very common with eCommerce stores that have products that fit into multiple categories. For example, you may have shop.com/baby-toys/rattles/awesome-blue-rattle
However, this product may also be available at shop.com/awesome-blue-rattle and maybe even again from shop.com/infant-gifts/awesome-blue-rattle and so on.
A canonical tag is you declaring to Google which of these URLs should rank when someone looks up ‘awesome blue rattle’. If you don’t tell Google which URL is the ‘preferred’ one, then they will either guess or just skip your site entirely. It is much better to exercise control of this yourself by setting up canonical links.
How to Improve Your Technical SEO?
Technical SEO is the backbone of your website, and it determines how stable and browseable your content is. It isn’t going to make you rank on its own, but it will be a damn site harder to rank without having a solid technical base.
Site Architecture
Use A “Flat” Site Structure
Generally speaking, a “flat” website structure is more conducive to SEO. The flat website structure means that users and search engine crawlers can reach any page on the website with only 4 clicks or less.
Keep It Simple
If your website has only hundreds of pages, the importance of a simple structure cannot be reflected. However, if you add a few thousand or more different pages to the website, we can see the importance of keeping the structure simple.
If you have a complex website structure like this:
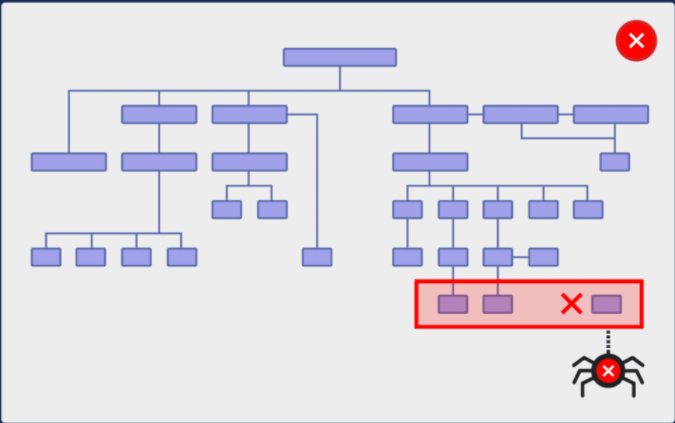
This is not only bad for SEO, but the user experience is also very poor. Imagine that you have just entered a random page of this website. How likely is it to find the page you need? Almost zero!
However, when your website structure is simple, users can easily find what they need.
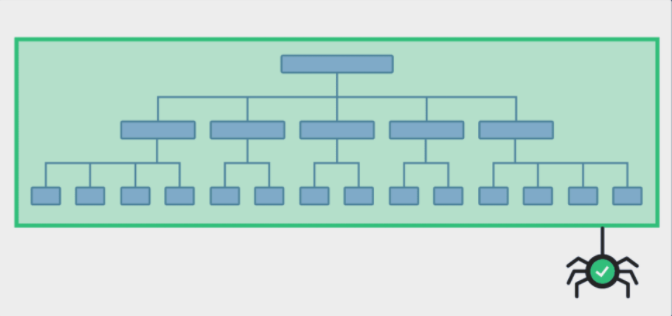
Use Category Pages
In the long run, category pages make the site structure very simple.
Want to create a new page? Add it to an existing category. And link to it from the category page.
Want to add a bunch of new pages? Create a new category. And a link to these new pages from this new category page.
If there is no classification structure, pages will be added randomly… This usually results in a complex website structure.
Note: If you run a relatively small website (less than 1,000 pages), you may not need to organize your pages by category. However, if you run an e-commerce website with a large number of pages, then classification is very important.
Use High-Weight Pages to Link New Content Pages
There are many different pages on a website, and these different pages have completely different page weights. There may even be situations where some third-level pages have a higher weight than the second-level pages.
For some newly created pages, because the content is not viewed by visitors, the content on the newly created pages does not have corresponding visitor data, and Google cannot obtain these visitor data to judge the weight, but the high-weight pages have been accepted and recognized by visitors. Therefore, If the new page is linked to the high-weight pages at this time, the corresponding benefits can be obtained.
Check Indexing
Using the Google search console, you can test how Google will crawl or present a URL on your website. You can use the “Coverage Report” to find out whether Googlebot visits a certain page on your website, how it will render the page, and whether it has been banned from accessing any web resources. This tool simulates what Google does in the regular crawling process, which can help debug crawling issues on your website
Check for Lost and Broken Links
Running a website audit of your own can identify broken pages, weird redirects, or any other structural deficits that your site may have. There is no shortage of tools available on the market that can help you crawl and audit your URL base. Or you can have our team handle this for you.
Speed Up Your Site
There are many ways to improve website speed. Many of these parts require a developer or technical SEO specialist to involve complex tasks. However, without the help of these people, you can also optimize your website by yourself or just contact us.
Identify Google Search Console Errors
Google Search Console divides errors into two categories: (site errors) and (URL errors). If there are multiple crawling errors on a website, your website trust will decrease, and it will even affect your ranking. The “Crawl Errors” function in Google Search Console can help you check wrong links, not only URL links but also DNS resolution failures, server links, robots.txt files, and other issues.
Check XML Sitemap Status
XML Sitemap can help search engines easily crawl the content of our website. It provides a machine-readable list of website content. Therefore, it plays an important role in search engine optimization.
Ensure that your website’s XML sitemap follows these guidelines:
1.Format your sitemap properly in the XML file
2.Make sure the sitemap follows XML protocol
3.Submit your sitemap to the Google Search Console
4.Sitemaps should include all pages updated on your website
Check HTTPS status
The safety of a website is a factor that search engines value very much, and HTTPS can add safe protection to our website. For this reason, search engines will prefer this kind of safe website in this respect. At the same time, we can also see from Google’s introduction to HTTPS-related content that Google places a higher value on websites that use HTTPS.
- Make sure you successfully complete the transition to HTTPS
- Purchase an SSL certificate
- New pages’ code update
- Check the source code of the new version page
- Check if 301 Redirects work
- Verify it in Google Search Console
- Continue to observe crawling, indexing, ranking, and traffic.
Ensure your site is Mobile-friendly
You can use The Mobile-Friendly Test of Google to verify whether the pages on the website meet the criteria for being marked as “mobile-friendly” on the Google search results page.
You can also view the Mobile Usability report of Google Search Console to modify and adjust the usability issues of mobile devices that affect the site.
Check robots.txt file
Robots.txt is a plain text file of the agreement between the website and the search engine. When a search engine spider visits a site, it first crawls to check whether robots.txt exists in the root directory of the site. The robots.txt file is very error-prone, so it is necessary to verify the robots.txt file.
To check if there is an error in a certain directory page of the website, you can put the directory or file blocked in the robots.txt file into the URL Inspection tool of Google Search Console. If it shows that it is blocked by the robots.txt file, it means that in the Sitemap file, there is at least one URL link is blocked by robots.txt.
To detect whether the website directory is blocked, you can use Google’s robots.txt detection tool to detect robots instructions. You also need to be careful when modifying robots instructions, because your modifications will affect other directory pages or files on the website.
Consultants Note: Be super careful with this if you are an inexperienced user!
Duplicate Content
Publishing original content to your website is critical to building an audience and improving search engine optimization. Then how to check duplicate content on your site?
1. Use the rel=canonical Tag
These tags tell search engines which specific URL should be regarded as the homepage of the page and solve the problem of confusion of duplicate content from the perspective of search engines.
2. Use 301 Redirect
This provides a simple search engine friendly way to send duplicate URLs to visitors when duplicate pages are deleted and the duplicate pages are not displayed.
3. Use the ‘noindex’ MetaURL Tag
This will tell search engines not to index these pages.
4. Use Google’s URL Parameters tool
This tool can help you tell Google not to crawl pages with specific parameters. If your website uses parameters as a way to deliver content to visitors, this may be a good solution, where most of the content is the same, but only slightly changed (e.g. title change, color change, etc.). With this tool, Google can easily know that your duplicate content is intentional, without having to consider search engine optimization.
Boost Your Technical SEO Strategy with Us
Technical search engine optimization can create a more favorable competitive environment, so please follow the indicators in our guide, and you will lay the foundation for the success of your online promotion.
Don’t know what tools to use? Here are some