Everyone knows that the ranking performance of a website in search engines is related to potential business opportunities. And as such, optimizing your website for search engine optimization (SEO) must not be taken lightly.
As a business owner or marketing manager, you must really want to know how well your website performs in terms of SEO, don’t you? That’s why you need to conduct an SEO audit on your website.
The SEO audit is a procedure to check whether the running website meets the basic requirements of an optimized website for search engines (achieving a good organic ranking on the search engine) at all levels, from how the website is constructed to the content of the website itself.
In this article, we will be discussing how to conduct an effective technical SEO audit on our websites to get the important pieces of information that will help you optimize your website.

How Do Search Engines Work on Websites?
First of all, you need to know the basic concept of a search engine and how it works on your website.
In order for a search engine to use their function, they utilize “crawlers”. It is a tool for crawling your website and analyzing them. This includes:
- What keywords (or phrases) the URL contains.
- The extent to which the content meets the searcher’s initial needs.
- How the content keeps searchers on the site.
- The speed and security of the website.
- The degree to which the website meets the SEO standards.
A Website SEO Audit Will Be Divided into 3 Aspects
Generally, an SEO audit is a big project and involving various elements on the website, but we can divide it into 3 aspects:
- Single Page SEO Audit: This consists of the content, performance, usability, and security status of a website;
- Website Technical SEO Audit, that is, the coding and other elements behind the page: website security performance, loading speed, image tags data, website architecture;
- Off-page SEO Audit: This aspect is related to what happens outside the site itself, such as trusted links, brand mentions, and website partners.
Single Page Audit Checklist
Single-page SEO work is the core of website optimization. We all know that content is the heart of SEO, but just creating content wouldn’t be enough to rank better and promote your business in a good way. Because what is content if it doesn’t reach anyone.
In a single-page audit, you will be going through the elements that make a page a page. By going through all of them and knowing what factors work together to cause your website ranking results can make it easy for you to make improvements inside your website.
Page URL
The first one is the page URL. We as humans or users usually identify a page by looking at the title and what it says of the page. But it’s not the case for the crawlers that we mentioned earlier. The first thing they see to identify a page is its URL, which is why you need to optimize your URLs.
It’s Best to Include Keywords
As we already established that crawlers identify the site primarily through the URLs, it should be obvious that it should include keywords.
Users use search terms or keywords to find the information through search engines and by laying out keywords in URL, you would help the crawlers identify your page to be related to that. That way, you can increase your relevance.
So make sure that you include the keywords in the URL.
Capitalization of URL Letters
As humans, uppercase letters and lowercase letters aren’t that different, generally. They all still read the same anyway, but that’s not the case if we are talking about machines.
The tools, bots, or crawlers, designed as machines, read an uppercase letter and lowercase letter as two different characters, unlike how we do.
That’s why, for some special servers, websites with the uppercase and the lowercase URL can be two completely different websites.
Just a little heads-up for all of us: When naming a URL for a page, it’s best to use all lowercase letters as they are easily readable and identifiable.
Use of URL Hyphens
If the URL of the page contains more than one word, you need to separate each word from the others. To do that, usually, we would use spaces, but it’s not the case here, we can’t use spaces.
To accomplish that feat, we are going to use hyphens “-” because that is how search engines interpret spaces. What about underscores “”? They are simply ignored.”
Not only that would read more clearly, this will also help the point that we’ve discussed before regarding inserting keywords in URL.
So, in most cases, we prefer to separate directory names or file names with hyphens “-“, and not to use underscores or other symbols.
Meta Title
If you are using search engines, you will see the title of the pages in blue-colored letters on the SERPs. That is what we call Meta Title. The length of this title should not exceed 60 characters for the English website. Why? Because that’s the limit of characters viewed as a title in SERPs is only that many (per Jun 2021). If you go beyond that limit, you will risk the title getting cut and would be read then interpreted differently.
It’s recommended to put your focus keyword in your Meta Title, but keyword-stacked titles are not of high value to users. The titles you choose should be concise and clearly displayed to users.
In addition to the concise title, the title and content are also required to be relevant and meet the user’s search needs, so as to help obtain better content display opportunities.
Meta Description
This is the part that may appear under the title of the search engine results and can include keywords as appropriate. The text is a brief description of the article or the excerpt, and the number of English characters should be between 50-160.
The user will not see the description after opening the webpage, but in order for search engines to better understand the website, the description is very necessary. It is a supplement to the title and plays a significant role in keyword optimization.
Filling in the website description correctly can not only improve the business relevance of the website but also enhance the matching of website keywords, which is conducive to website keyword ranking.
Note: In the description, you can also use a small gimmick to attract users’ attention and clicks. For example, you can provide users with some tools, materials, cases, etc.
Keywords
Setting keyword tags is more of an auxiliary function, and will not be displayed in the search results.
When refining keywords, you can repeat the content of the title, usually, about 2 – 3 will be fine.
Keywords are relatively less important than titles and descriptions, but it is definitely better to fill in them in accordance with the specifications.
At the very least, by using keyword tag, you can help yourself optimizing the content to increase its relevance with related keywords.
H1 Tag
H1 tag is the first heading tag that would signify a new beginning of a new topic on a page. Usually, it appears on top of the page in a form of a page title.
It is recommended to use only one H1 on a single page as it would make the page more focused content-wise and can rank better for a specific group of keywords.
Make Every H1 Tag Unique
Each page should have a unique H1 because each page should contain unique content. As we mentioned earlier, your H1 tag acts as the title of the page, so make sure your H1 directly explains the content of the page.
You need to note that while H1 also acts as the title of the page, it doesn’t have the same limitation as to the meta title. So you can use this to your advantage to make a more elaborate and interesting title to keep the users interested in your website.
Insert Keywords in The Title
You need to maximize your use of keywords, and one place that it can be really impactful to put your keyword in is H1 tags. It is because search engines will pay close attention to the keywords in the H1 tag to determine their relevance.
Like the one that begins a topic on a page, they should cover the main theme of the page. avoid using keywords that have nothing to do with the content of the page. This is also a factor in whether the page really answers the query of the users or not.
H2, H3 Tags
The tag setting of the paragraph headings in the article needs to be set to H2 or H3 according to the level of the depth of the discussion. To maximize its use, the text needs to contain keyword variants of the focus keyword that appears on the H1, that is, similar words or synonyms or just related to the main theme.
Image
Images are an element that not only makes the page look better, they can also be a medium to deliver a certain piece of the situation or just illustrate something. The use of an image cannot be taken lightly since we are mostly a visual being that relies on what we look at. So using images can really make the information easily understood.
However, you can’t just put the image without any considerations, adjustments, and configurations. Have a look at these noteworthy things:
- When uploading a picture, remember to define the size of the picture (the width and height in px).
- Add “Alt” to any picture to tell search engines what the picture is about, and Alt text must have alternative content so that there is a text description image when the image is not displayed.
- The image file name and title should include keywords. The file size should not exceed 100KB. In fact, smaller images should be 30-40KB in size.
- If an image is too large, consider using image processing software to optimize it. This can include saving it in a web-friendly format, which can significantly reduce the space required for the image, ensuring your customers are not deterred by slow loading times.
And yes, as the note says, images can affect the loading speed of a page, so make sure to keep that in mind.
Internal link
An internal link is a link that connects one page to another within the same website. Internal links may indicate how each page is relevant to each other and search engine crawlers will go through these links to determine that.
Use Descriptive Anchor Text
Anchor text is the part of the link that is visible to website visitors. In order for website visitors and search engines to clearly understand their expectations when they click on the link, you need to use descriptive anchor text.
For example, if you link to a page located at “domain name/pets/dogs.html”, the anchor text can simply say “Pet Dog”. This way, people can know what information they will find if they click the link.
Avoid Links in Forms and Internal Search Boxes
It’s important to remember that search spiders will not attempt to submit forms. This means that search engines cannot see any content or links that can be accessed through the form.
Search spiders will also not try to perform searches to find content on your website. Therefore, it’s important not to hide anything behind the internal search box.
Use Natural Links
Make sure that internal links are natural to the reader. When readers see an information link that matches the context of the content, they are more likely to click that link and browse other content on your website.
After all, if someone is reading an article about SEO, it might not make sense to direct them to a page about makeup tips. There’s a slim chance that they will click it.
When you include natural links to other pages on your website, visitors will be more involved in your website and will likely spend longer on your website.
Website Technical SEO Audit Checklist
Next up we are going to talk about the technical side of SEO and how you can improve them. Even though the content is the core of optimizing a site, the technical side like indexing is crucial. After all, it indicates whether the pages of your site are registered and accessible through the search engine or not.
So let’s get on and see the technical aspect of SEO audit.
Index Checking
As we mentioned, indexing indicates whether your page is registered and accessible through search engines or not. It is usually marked as indexed or non-indexed.
You need to make sure that the pages you want to rank on search engines to be indexed so they can rank for the keywords they contain.
Number of Indexed Pages
First of all, you should know how many pages of your website should be indexed.
To check this, go to the Google Search Console in your Google Analytics account control panel and look for the index count in the left column. Here we need to verify whether the number of pages on the website is consistent with the number included, and if they are inconsistent, we need to resolve them.
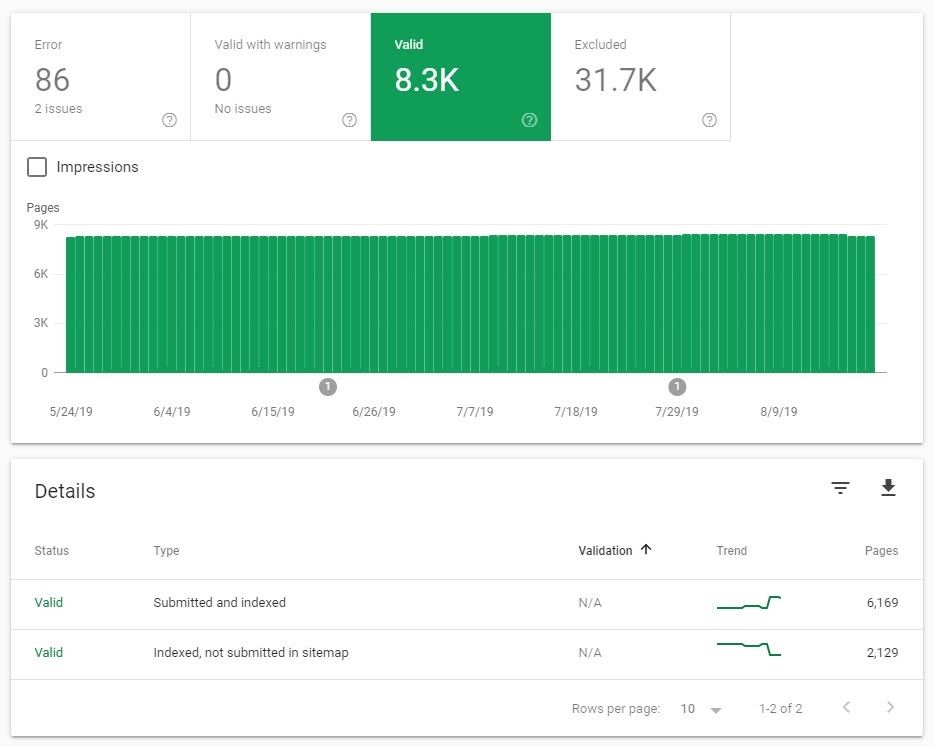
The Google Search Console Coverage report provides the number of crawled pages, pages that cannot be indexed, and crawled error pages. It also displays pages that are not indexed in the XML sitemap and pages that are not indexed in the XML sitemap.
Page Value
Not all pages are valuable for organic search. For example, internal search and terms of use pages, both of which are useful to users on the site, but should not be indexed for display in search results.
Products, categories, and certain filtered pages are also valuable because these pages contain keywords that people will search for, such as “black cotton sweaters”
Analyze your Coverage report to ensure that robots can crawl and index valuable pages without crawling or indexing other irrelevant web pages. Ensure that valuable pages are indexed, while the not valuable ones are excluded.
Duplicate Content
If the same content is displayed on different pages, it is duplicate content. This will reduce the link weight of duplicate content pages, cause internal web pages to compete with each other, and affect the value of crawling. Therefore, it is recommended that you eliminate duplicate content as much as possible.
Sitemap Check
It can be said that a sitemap is like a blueprint of your website that helps the search engine spiders and crawlers to find, crawl and index the content of your website. It can also be used to tell the search engine which pages are more important.
Usually, crawlers will start from your homepage, but sometimes they can also crawl through the sitemap. Therefore, you need to monitor and optimize your sitemap too.
Sitemap Should Include The Most Important Pages
The most important page on the website must not be omitted. If the important page is not displayed on the Sitemap, this means that the visitor may not find the information he needs. Then the visitor’s favorability of the website will decrease.
Ensure that All Links on The Site Map Are Correct And Valid
If the links appearing in the site map are dead links or broken links, the impact on search engines is very bad. Check every link on the Sitemap to avoid this situation.
Add Sitemap into Robots.txt File
When a search engine spider comes in to crawl a webpage, the first thing it visits is the Robots.txt file. If the sitemap is placed in the robots.txt file, the spider will access the site map earlier and faster, which greatly improves the crawling efficiency of the spider.
Evaluate site structure
Crawlers of search engines prefer websites to arrange their content level by level according to the level of categories.
Does the hierarchical arrangement of website URLs make sense?
If the composition of the URL lacks a logical relationship and the site structure needs to be rearranged, the original URL can be rewritten through redirects.
Please note that the correct URL does not contain capital letters, underscores, and punctuation (including special characters), search engines cannot recognize these elements.
Website Security
Search engines also attach great importance to the protection of visitors’ privacy.
An HTTPS website indicates that it has an SSL (Secure Socket Layer) certificate, which means that the visitor’s data is secure between the browser and the site server.
When switching HTTP to HTTPS, you need to pay attention to these issues:
- Ensure to make a redirect for each link, which is 301 or 302, so that search engines can better crawl the pages.
- The authentication will be successful only after the entire site is switched to HTTPS. Once some links are not properly switched, the authentication will fail.
Crawl Availability Issue
Google Search Console will display URLs with 404 errors (ie pages not found) and other pages with accessibility warnings. We need to clean up these pages one by one.
The Crawl Stats report in Search Console shows you statistics about Google’s crawling history on your website. For instance, how many requests were made and when, what your server response was, and any availability issues encountered.
You can use this report to detect whether Google encounters serving problems when crawling your site.
Loading Speed
This factor is becoming more and more important, instantly becoming the first core element of the website.
This speed specifically refers to the loading time of the webpage, that is, the time required for the webpage to be displayed after entering the URL.
A web page with a long loading time brings two disadvantages:
- Search engines can only crawl less content in a limited time.
- The user experience is poor. People don’t have much patience to wait for slow web pages.
It is recommended to use Google’s PageSpeed Insights, which can thoroughly test the website’s performance level.
Off-Page SEO Audit Checklist
The off-site audit is different from the on-site audit, and it cannot directly determine whether the website meets the SEO requirements.
For example, a link that does not seem to have brand value may have a greater effect on rankings, while some links that appear to have brand value may not help rankings.
The following are three important aspects:
- Domain Authority: The domain name ranking evaluation value developed by MOZ, between 1-100, the higher the score, the higher the ranking.
- Backlinks: Where do the backlinks of the website come from? How authoritative are they?
- Brand reputation: Do your corporate brand and corporate name often appear on well-known platforms/media platforms. If your brand often appears on authoritative websites, it will help your website’s ranking.
Audit Your Website Frequently
An SEO audit is a crucial process that ensures that all basic work on the website has been done correctly. It seems like none of these steps are easy. Even so, it’s definitely worth the time of the owner of the website or the marketing manager to start an SEO audit as a way to evaluate their efforts so far.
Would you like a professional and comprehensive technical SEO audit? Feel free to reach out to our experts, and they will be happy to assist you!
“>